Bone grafting is extremely important to prepare your jaws for your implants.
Why: All implants require very strong stable bone around them to last for many years. If your bone is weak, or missing from infection or time, you will need bone grafting first. This takes time to heal and requires your body’s natural physiology to work.
How: There are three ways to do bone grafting:
Autografting
Take bone from your body and move it where you need replacement bone.
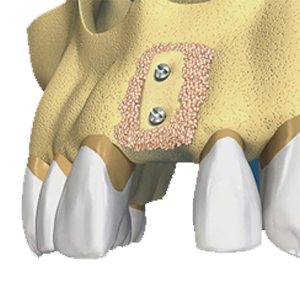
Allografting
Use donated bone from another person to develop bone where you are missing.
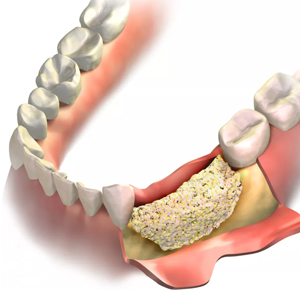
Induction
Use Proteins and Bone Enhancing agents make your body grow its own bone.
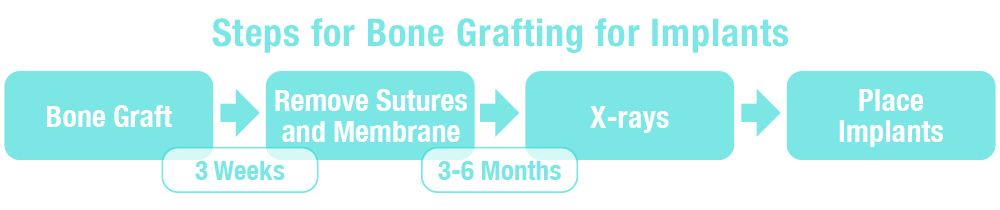
What to Expect With
Bone Grafting
Major Bone Grafting
Bone grafting can repair implant sites with inadequate bone structure due to previous extractions, gum disease, or injuries. The bone is either obtained from a tissue bank or your own bone is taken from other areas of the the jaws. Sinus bone grafts are also performed to replace bone in the posterior upper jaw. In addition, special membranes may be utilized that dissolve under the gum to protect the bone graft, as well as encourage bone regeneration. This is called guided bone regeneration, or guided tissue regeneration. Minor bone grafting can often be preformed in an office setting.
Minor Bone Grafting
Major bone grafts are typically performed to repair larger defects of the jaws. These defects may arise as a result of traumatic injuries, tumor surgery, or congenital defects. Large defects are repaired using the patient’s own bone or biological technology. This bone is harvested from a number of different areas depending on the size needed. The skull (cranium), hip (iliac crest), and lateral knee (tibia), are common donor sites. These procedures are routinely performed in an operating room and require a hospital stay. Our surgeons are trained to perform bone grafts from minor, single tooth sites, to major grafting and reconstruction.
Call 803-699-5900 to schedule your bone grafting consultation.
Contact Us
Columbia: 803-699-5900
Orangeburg: 803-534-5444
Camden: 803-398-9900
